Summary of 2020 Term Asset-Backed Securities Loan Facility (TALF)
On March 23, 2020, the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve (Board), with the approval of the Secretary of Treasury, authorized the Federal Reserve Bank of New York (the FRBNY) to establish and operate the Term Asset-Backed Securities Loan Facility (the 2020 TALF) as a means of facilitating the issuance of asset-backed securities (ABS) and stabilizing American ABS markets disrupted by the spread of COVID-19.
TALF loans may provide a low-cost financing option for auto financing companies, equipment financing companies, insurance companies, and other companies that finance small business loans and/or commercial loans.
Under the 2020 TALF, the FRBNY will commit to lend to a special purpose vehicle (SPV), on a recourse basis, and the Department of the Treasury (Treasury) will invest $10 billion in equity in the SPV. The SPV will then makeup to $100 billion of loans available to Eligible Borrowers (defined below) on a nonrecourse basis and secured by Eligible Collateral (defined below). Below is a summary of the 2020 TALF; additional regulations and guidance from Treasury and the FRBNY are expected in the coming days.
Eligible Borrowers |
All companies owning Eligible Collateral (defined below) that are organized in the United States or under the laws of the United States, and which have significant operations in and a majority of their employees based in the United States. Eligible Borrowers must also maintain an account relationship with a primary dealer. |
|---|---|
Eligible Collateral |
U.S. dollar denominated cash (not synthetic) ABS (i) having a credit rating in the highest long-term (for mortgage-backed ABS) or the highest short-term (for nonmortgage-backed ABS) investment-grade rating category from at least two (2) nationally recognized statistical rating organizations (NSROs),[1] and (ii) not having a credit rating below the highest investment-grade rating category from an eligible NSRO. The underlying credit exposures of the ABS must be one of the following:
All or substantially all of the underlying credit exposures underlying the ABS must have been originated by a U.S. company and the issuer of the Eligible Collateral must also be a U.S. company. With the exception of collateralized mortgage-backed securities (CMBS), all eligible ABS must be issued on or after March 23, 2020. Eligible CMBS must have been issued prior to March 23, 2020. The following additional requirements also apply to the Eligible Collateral:
|
Conflicts of Interest |
Neither the Eligible Borrowers nor the issuers of Eligible Collateral may be entities in which the President, the Vice President, the head of an Executive Department, a member of Congress, or a spouse, child, son-in-law, or daughter-in-law of any of the foregoing persons directly or indirectly holds a controlling interest. |
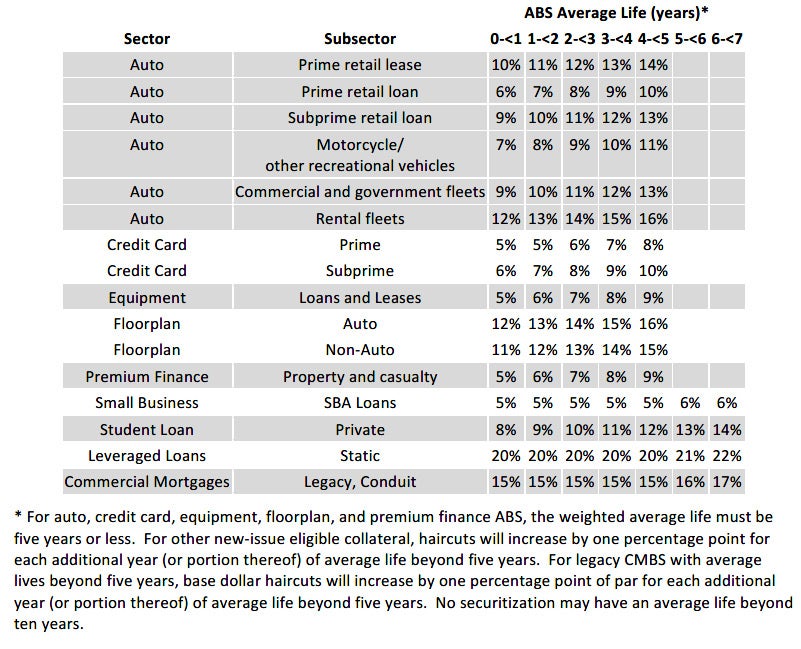
Collateral Valuation |
Eligible Collateral will be valued and assigned a haircut based on its sector, subsector, and weighted average life in accordance with the Schedule attached to this Summary. |
Pricing |
Pricing will vary depending on the type of Eligible Collateral as follows:
Pricing for other Eligible Collateral will be provided by the Federal Reserve at a later date. |
Fees |
The SPV will assess an administrative fee in an amount equal to 10 bps of the Loan amount on the settlement date for collateral. |
Term |
Each Loan will have a three (3) year term. |
Prepayment |
Loans are prepayable in whole or in part at the option of the Eligible Borrower. |
Substitution of Collateral |
Substitution of collateral for the Loan will not generally be allowed. |
Termination Date |
The SPV will continue to make Loans until September 30, 2020 (unless the Board and the Treasury Department extend the 2020 TALF). |
Haircut Schedule
[1] A.M. Best Rating Services, Inc., DBRS, Inc., Fitch Ratings, Inc., Egan-Jones Ratings Co., Japan Credit Rating Agency, Ltd., HR Ratings de México, S.A. de C.V., Kroll Bond Rating Agency, Inc., Moody’s Investors Service, Inc., and S&P Global Ratings.
Contacts
- Related Practices

